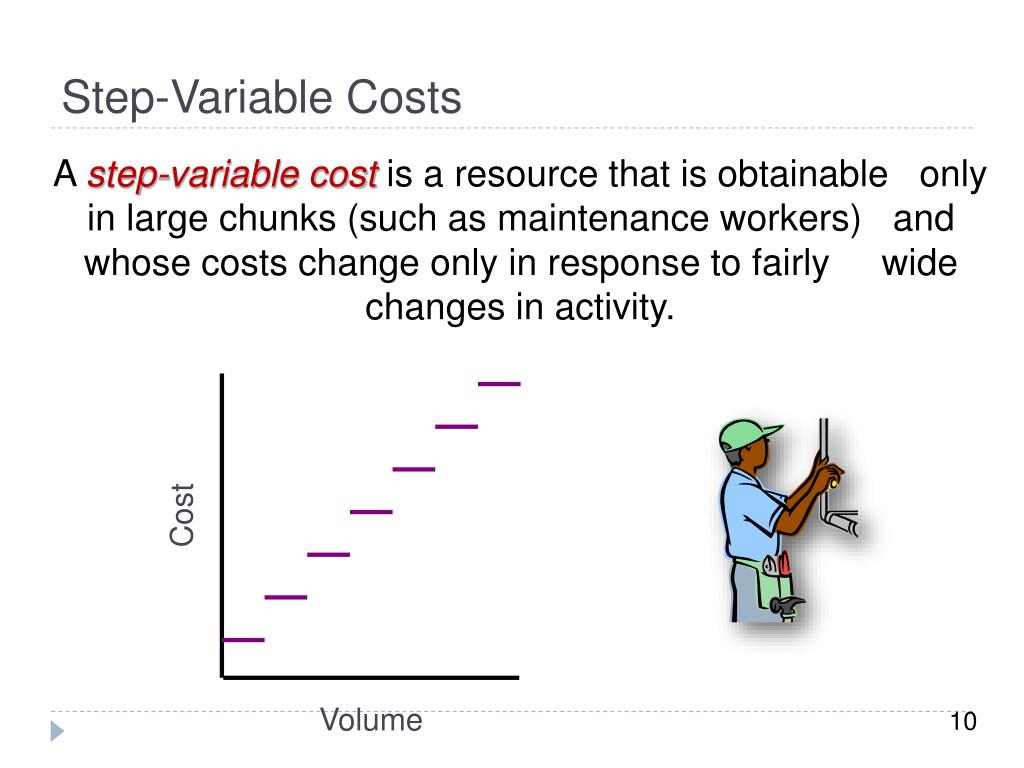
Maintenance costs will thus increase with every 10,000 unit increase in production levels. For example, a cost can be say $100 up to 500units, increase to $185 for 501 to 1,000 units and to $260 if output crosses 1,000 units. The cost with such a pattern of increase would be classified as step variable cost.
Mixed Costs and Stepped Costs
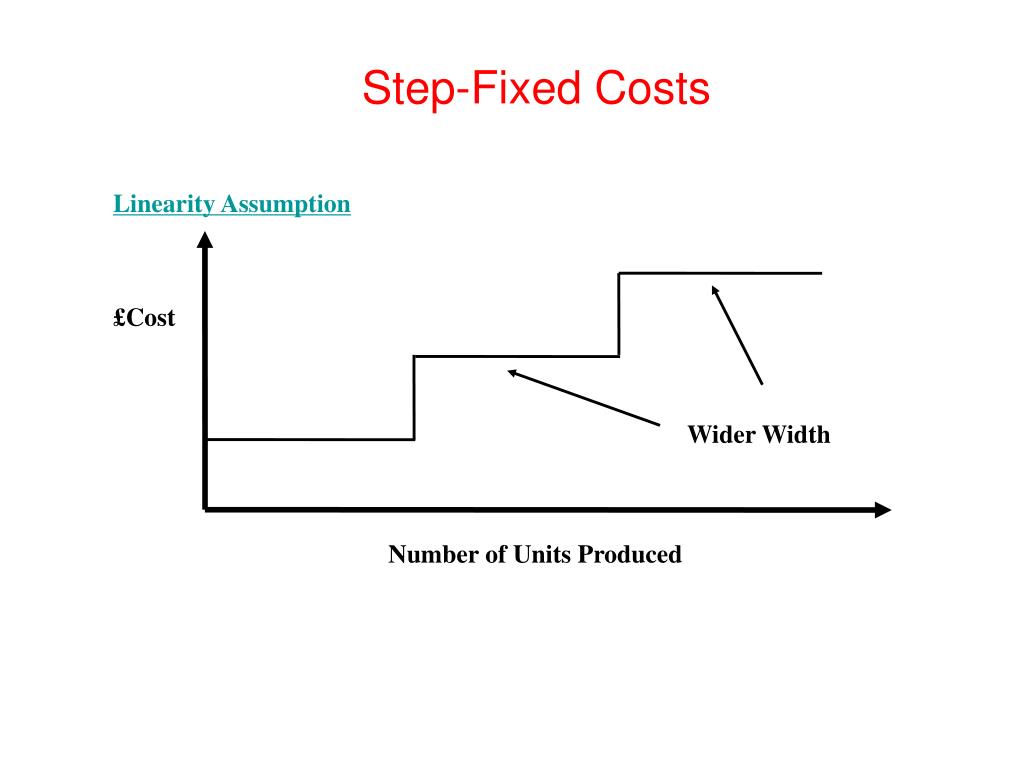
A cost that changes with the level of activity but is not linear is classified as a stepped cost. Step costs remain constant at a fixed amount over a range of activity. The range over which these costs remain unchanged (fixed) is referred to as the relevant a $10,000 obamacare penalty doubtful range, which is defined as a specific activity level that is bounded by a minimum and maximum amount. Within this relevant range, managers can predict revenue or cost levels. Then, at certain points, the step costs increase to a higher amount.
Step Costs
- The term step-variable costs is a synonym for semi-variable or semi-fixed costs and contemplates an increase in costs with an increase in capacity.
- If erasers cost 20 cents each, the variable eraser cost of making 1,000 pencils is $200 (1,000 X $.20).
- They help managers understand how costs change as production or activity levels vary, enabling more accurate budgeting and strategic decision-making.
- For instance, wages often act as a stepped variable cost when employees are paid a flat salary and a commission or when the company pays overtime.
If our pencil maker hires a bookkeeper for $10,000, this is a fixed cost because the cost stays the same regardless of the number of pencils that are produced. For example, if a processing facility capacity is 100,000 units of production, 100,000 is the upper limit of the range for the fixed cost. Production over 100,000 will require additional facility investment which will mean more fixed costs. If the company hires a second quality inspector, they would be stepping up their fixed costs.
AccountingTools
Each month, Bert will recognize 1 ÷ 12 of this insurance cost as an expense in the period in which it is incurred (Figure 6.38). Discretionary fixed costs generally are fixed costs that can be incurred during some periods and postponed during other periods but which cannot normally be eliminated permanently. Both of these costs could potentially be postponed temporarily, but the company would probably incur negative effects if the costs were permanently eliminated.
If activity levels spike upward or downward unexpectedly, costs can increase or decrease disproportionately. They help managers understand how costs change as production or activity levels vary, enabling more accurate budgeting and strategic decision-making. Where Y is the total mixed cost, a is the fixed cost, b is the variable cost per unit, and x is the level of activity. A fixed cost is an unavoidable operating expense that does not change in total over the short term, even if a business experiences variation in its level of activity.
Step Cost Explained
For example, Carolina Yachts has production supervisors who oversee the manufacturing process but do not actively participate in the construction of the boats. Their wages generally support the production process but cannot be traced back to a single unit. For this reason, the production supervisors’ salary would be classified as indirect labor. However, if you are considering the supervisor’s salary cost on a per unit of production basis, then it could be considered a variable cost.
Step-variable CostsStep-variable costs are costs that are constant over a range of production. If one employee can make 10,000 pencils, then the employee’s wage is constant over a production range of one to 10,000 pencils. If you make 25,000 pencils your cost triples because you need three employees. As you have learned, much of the power of managerial accounting is its ability to break costs down into the smallest possible trackable unit. In many cases, businesses have a need to further refine their overhead costs and will track indirect labor and indirect materials.
Let’s use a catering business as an example to illustrate the concept of step variable costs. When opening a new production facility, business owners will need to consider the additional step costs in employee salaries and equipment. Health care and pension contributions can also fluctuate when staffing levels rise or fall below a certain threshold. If you need to delay the sudden jump in step costs, consider offering overtime to employees. Overtime shifts can help you produce more units without hiring additional full-time staff.